The classic presentation of pulmonary fibrosis is slowly progressing shortness of breath (“dyspnoea”) with a chronic non-productive (dry) cough. The shortness of breath is typically worse on exercise and exertion.
There are various other signs and symptoms though including:
> Fatigue & lethargy
> Loss of appetite
> Weight loss
> Chest pain
> Wheezing
> Low grade fever & muscle pains
Diagnosing pulmonary fibrosis
Various tests can be performed in order to diagnose pulmonary fibrosis, these may include:
Spirometry (‘breathing and blowing tests’): these simple breathing tests may show a restrictive pattern with a reduced total lung volume.
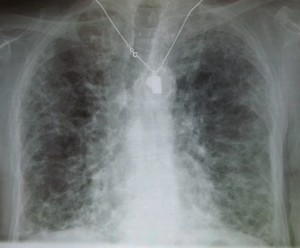
Chest x-ray: some signs may be visible on a chest x-ray or one may be performed to rule out any other lung disease.
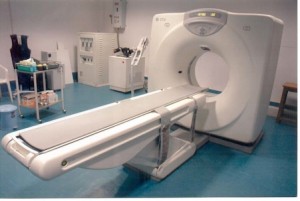
Computed Tomography (CT) scan: this may also be called a HRCT, or high resolution CT scan. A CT scan shows more detail than a chest x-ray, but may not always be required.
Lung biopsy: A lung biopsy is an invasive procedure and not always required if there is clear evidence of pulmonary fibrosis on x-ray or CT.